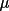|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| astar [a] | spherical absorption A* values |
| tbar [a] | spherical T values |
| diff [a] | diffractometer description |
| orient [a] | crystal orientation |
| orface [b] | microscope orientation |
| facept [b] | face described by three points |
| face [b] | face described by
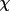 , ,
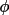 , and
distance , and
distance |
| faceom [b] | face described by
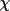 , ,
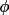 , ,
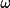 and
distance and
distance |
| faceml [b] | face described by Miller indices anddistance |
| grid [c] | Gaussian grid description |
|
[a] Optional according to mode: diff and orient are mandatory for Gaussian and analytical corrections and are in fact order dependent (the diff line MUST precede the orient line for correct operation) [b] Only one of the methods orface, facept, face or faceml may be used to specify the faces of the crystal. [c] Used only for the Gaussian integration method. | |
| ABSORB | Option | Code | |||
absorption coefficient in mm
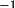 |
|
|
auto [a] | ||
| absorption method |
|
Gaussian integration | |||
analyt
|
analytical method | ||||
|
spherical crystal [b] | ||||
|
cylinder | ||||
|
user tables | ||||
| application of absorption |
|
do not apply | |||
irel
|
apply to
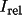 |
||||
|
apply to
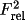 |
||||
|
apply to
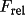 |
||||
| store T on bdf |
|
no | |||
tbar
|
yes [b] | ||||
| print reflection data |
|
|
print n hkl |
99999
|
|
| limit reflections processed |
|
|
process n hkl |
99999
|
|
| dataset specification |
|
|
dataset number |
1
|
|
| precision scale factor [c] |
|
|
scale distance and μ | ||
crystal plot view on file
abs
|
|
stereo view | projection | ||
| radius of crystal in mm |
|
|
|||
|
[a] Default is to calculate
[b] If the
[c] This option is used to avoid rounding errors for small crystals. | |||||
| astar [a] | 1-19 | values of A* corresponding to 0°,5°, 10°, ..., 90° | |
[a] More than one astar line may be used. | |||
| tbar [a] | 1-19 | values of T corresponding to 0°, 5°, 10°, ..., 90° | |
[a] More than one tbar line may be used. | |||
| diff [a] | 1 | sense of rotation of the2
 circle circle |
c
|
clockwise | |
|
anti-clockwise | ||||
| 2 | sense of rotation of the
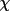 circle circle |
c
|
clockwise | ||
|
anti-clockwise | ||||
| 3 | sense of rotation of the
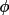 circle circle |
c
|
clockwise | ||
|
anti-clockwise | ||||
| 4 | sense of rotation of the
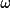 circle circle |
c
|
clockwise | ||
|
anti-clockwise | ||||
| 5 | sense of rotation of the
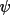 circle circle |
c
|
clockwise | ||
|
anti-clockwise | ||||
| 6 | value of
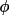 at at
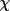 = 90
degrees = 90
degrees |
0
|
|||
| 7 | minimum possible
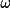 (-180 < (-180 <
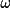 <
180) <
180) |
-48
|
|||
| 8 | maximum possible
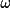 (-180 < (-180 <
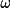 <
180) <
180) |
58
|
|||
| orient | 1-3 | hkl indices of first orienting reflection | |
| 4 | angle χ of first orienting reflection [a] | ||
| 5 | angle φ of first orienting reflection | ||
| 6-8 | hkl indices of second orienting reflection | ||
| 9 | angle χ of second orienting reflection | ||
| 10 | angle φ of second orienting reflection | ||
[a] Angles in the bisecting mode. (For CAD see Ch. II of the CAD User's Manual.) | |||
| orface [a] | 1-3 | x, y, z coordinates of first point on orienting face | |
| 4-6 | x, y, z coordinates of second point on orienting face | ||
| 7-9 | x, y, z coordinates of third point on orienting face | ||
[a] If the orface - facept method is used for entering face data, two orface lines must be used. The first contains the coordinates of three points on a plane parallel to the first orienting reflection given on the orient line. The second orface line contains the coordinates of three points on a plane parallel to the second orienting reflection given on the orient line. | |||
| facept | 1-3 | x, y, z coordinates of first point on bounding face | |
| 4-6 | x, y, z coordinates of second point on bounding face | ||
| 7-9 | x, y, z coordinates of third point on bounding face |
| face | 1 |
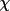 for bounding
face
(angles in the bisecting
mode) for bounding
face
(angles in the bisecting
mode) |
|
| 2 |
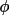 for
bounding face for
bounding face |
||
| 3 | distance to origin from bounding face in mm |
| faceom | 1 |
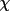 for bounding
face
(angles in the
bisectingmode) for bounding
face
(angles in the
bisectingmode) |
|
| 2 |
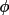 for
bounding face for
bounding face |
||
| 3 |
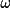 for
bounding face for
bounding face |
||
| 4 | distance to origin from bounding face in mm |
| grid [a] | 1-3 | number of grid points in x, y, z directions |
8
|
||
| 4 | method of exponentiation |
0
|
library function | ||
|
table look-up | ||||
[a] The grid line is used only if the Gaussian method is selected. Only the intervals 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 24, or 32 are possible. | |||||